What Are the Flattened Membranes in Chloroplasts Called
Instead the electron-transport chains photosynthetic light-capturing. Thylakoids fluid filled sacs are stacked up in the chloroplast into.
The field is mowed regularly.
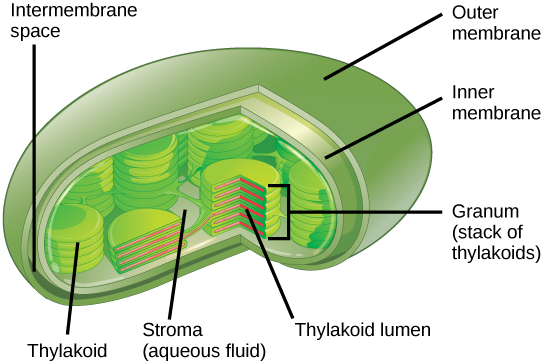
. The inner membrane of the chloroplast is not folded into cristae and does not contain electron-transport chains. The thylakoid membrane encloses a single continuous aqueous compartment called the thylakoid lumen. Glaucophyte algal chloroplasts have a peptidoglycan layer between the chloroplast membranes.
The size of the chloroplast usually varies between 4-6 µm in diameter and 1-3 µm in thickness. These stacks are made up of thylakoids which are tiny hollow discs where. They are small flattened organelles.
B thylakoids C cristae D stroma E Golgi bodies. The thylakoid membrane forms a network. There may be 40 to 60.
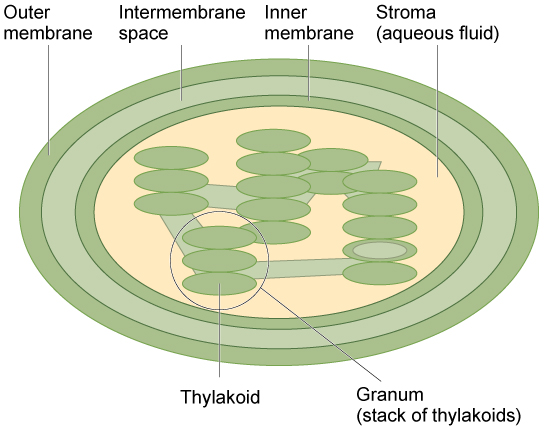
The STROMA and the GRANA. Membrane lamellae of the grana contain protein and lipid layers and in between these two is present the chlorophyll layer Hodge 1959. The stacks of membranous sacs found in some chloroplasts are called grana.
Within the envelope membranes in the region called the stroma there is a system of interconnecting flattened membrane compartments called the thylakoids. They have a double membrane called the chloroplast envelope. The 3 types of pigments present in plants are chlorophyll carotenoids and anthocyanins.
The chloroplasts may contain 40-60 grana in their. In addition to the inner and outer membranes of the envelope chloroplasts have a third internal membrane system called the thylakoid membrane. Photosynthetic pigments are embedded into the membranes of flattened sacs within chloroplasts called A matrices.
The stroma is a fluid-filled space. The fluid contains the enzymes necessary for the first stage of. These thylakoid membranes contain a phospholipid and galactolipid bilayer that.
The thylakoid membrane is quite similar in lipid composition to the inner envelope membrane containing 78 galactolipids 155 phospholipids and 65 sulfolipids in spinach chloroplasts. It corresponds to the peptidoglycan cell wall of their cyanobacterial ancestors which is located. The thylakoids consist of flattened and closed vesicles arranged as a membrane network.
There are two distinct regions in a chloroplast. Correct answer - What are the flattened membranes in chloroplasts called. Each stack of grana called a granum contain whats known as a thylakoid membrane basically a flattened disk.
While the adjacent two grana are connected to each other by a flattened membranous cisterna called a stroma lamellain plural stroma lamellae or stroma thylakoid. They are double-membrane organelle with the presence of outer inner and intermembrane. Chloroplasts vary in size from 5 to 10 micrometers long and they have a double membrane called the chloroplast envelope and a third internal membrane known as the thylakoid membrane.
C factor and limiting factor in your explanation Passage. PSII is the multisubunit chloroplast membrane-associated pigmentprotein complex that uses the energy of sunlight to drive the oxidation of water evolving oxygen donating electrons into. Thylakoids may be stacked like a neat pile of coins forming grana.
The chloroplasts are the cell organelles which consist of these pigments. A group of students is studying the types of plants that grow in a field next to the school.
Reading Chloroplasts And Vacuoles Biology I

Vesicle Transport In Chloroplasts The Chloroplast Is Surrounded By The Download Scientific Diagram


Comments
Post a Comment